Understanding ADHD Therapy for Children: A Complete Guide
When a child struggles with ADHD, finding the right support can transform their entire future. Let’s explore how specialized therapy helps children harness their unique strengths and overcome challenges.
What is ADHD in Children?
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is more than just difficulty focusing or excess energy. It’s a neurodevelopmental condition that affects how a child’s brain processes attention, manages impulses, and organizes information. Understanding ADHD as a difference in brain functioning, rather than a deficit, helps parents and children approach therapy with hope and confidence.
Signs Your Child Might Need Support
Every child shows ADHD differently, but common patterns often emerge:
Attention Challenges:
- Difficulty maintaining focus during structured activities
- Seemingly not listening when spoken to directly
- Struggling to complete tasks or homework
Hyperactivity Signs:
- Constant motion or fidgeting
- Difficulty staying seated
- Talking excessively or interrupting others
Executive Function Issues:
- Problems with organization
- Frequently losing important items
- Struggling with time management
How ADHD Therapy Helps Children Thrive
Modern ADHD therapy combines several evidence-based approaches to support children’s development. Here’s how therapeutic interventions make a difference:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps children understand the connection between their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Through age-appropriate activities, children learn to:
- Recognize challenging thought patterns
- Develop problem-solving skills
- Build self-awareness and confidence
Play-Based Interventions Children learn best through engagement and play. Therapeutic play helps develop:
- Improved attention span
- Better impulse control
- Enhanced social skills
- Stronger emotional regulation
The Journey Through ADHD Therapy
Successful therapy follows a structured path while remaining flexible to each child’s needs:
Initial Phase (1-2 Months) During this foundation-building period, children learn basic coping strategies while therapists assess their specific challenges and strengths. Parents receive education about ADHD and initial support strategies.
Skill Development (2-4 Months) As children become comfortable with basic techniques, therapy focuses on:
- Building organizational skills
- Developing study strategies
- Improving social interactions
- Strengthening emotional regulation
Maintenance Phase Once core skills are established, sessions focus on:
- Reinforcing successful strategies
- Addressing new challenges
- Building independence
- Preparing for transitions
School Success Strategies
Effective ADHD therapy includes practical academic support:
Classroom Strategies: Children learn techniques for staying focused and organized during school hours. This includes:
- Note-taking methods
- Organization systems
- Active listening skills
- Participation strategies
Homework Management: Therapeutic approaches help establish:
- Structured study routines
- Task-breaking techniques
- Time management skills
- Environmental modifications
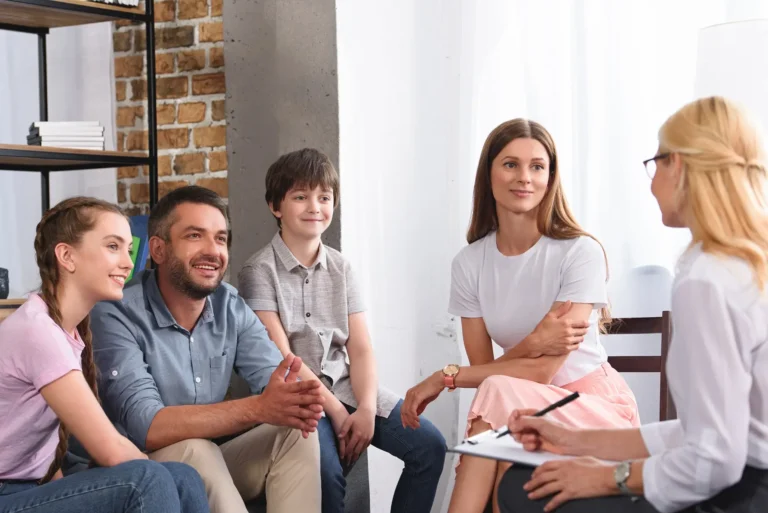
Supporting the Whole Family
ADHD affects the entire family system. Successful therapy includes:
Parent Education: Understanding ADHD helps parents:
- Recognize triggers and patterns
- Implement effective strategies
- Support their child’s growth
- Maintain consistent approaches
Family Communication: Improving family dynamics through:
- Clear communication methods
- Consistent routine establishment
- Positive reinforcement techniques
- Stress reduction strategies
Long-Term Benefits of ADHD Therapy
Research shows that early intervention through therapy provides lasting benefits:
- Improved academic performance
- Better social relationships
- Enhanced self-esteem
- Stronger family connections
- Reduced anxiety and frustration